What is Carotid Artery Disease?
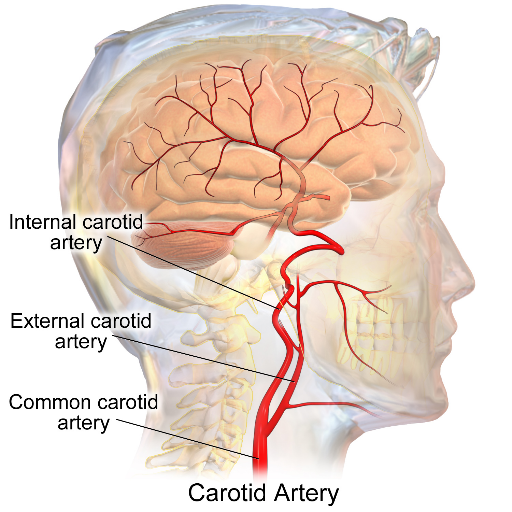
Carotid artery disease is a disease in which fatty deposits, called plaque, builds up inside your carotid arteries, which are the arteries that deliver blood to your head and brain. Carotid artery disease is serious because the blockage caused in these arteries increases your risks of having a stroke. A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is cut off, seriously reduced, or interrupted.
Strokes deprive your brain of oxygen, which within minutes, your brain cells start to die. Strokes can impair the parts of the body that brain cells control. Therefore, strokes can lead to brain damage, speech problems, vision problems, long-term disability such as paralysis, or death. Stroke is the leading cause of permanent disability, and one of the most common causes of death in the United States.
Symptoms:
Many times, especially in early stages, carotid artery disease does not often produce any signs or symptoms. This disease can go unnoticed until it is serious enough to cause a stroke. Thus, signs and symptoms of stroke include: sudden dizziness, sudden numbness or weakness in the face or side of the body, sudden trouble speaking, sudden trouble understanding, sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes, and/or a sudden severe headache.
Causes:
Major factors that contribute to damage in the inner layers of the carotid arties (which can lead to carotid artery disease) include:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- High cholesterol levels in the blood
- Diabetes or insulin resistance (high levels or sugar in the blood)
Treatments:
Treatments will depend on how severe the disease is, your age, your symptoms, and your overall health. Talk to your doctor if you have any risk factors for carotid artery disease, even if you do not have any signs or symptoms. The goal of treatment is to stop the disease from worsening and of course, preventing stroke. Treatments may include lifestyle changes, medicines, and/or medical procedures such as TransCarotid Artery Revascularization (TCAR) or artery angioplasty & stenting.

